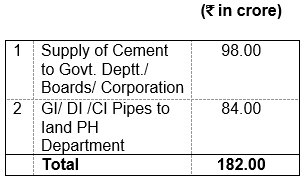
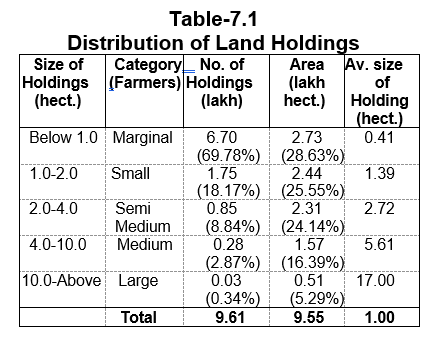
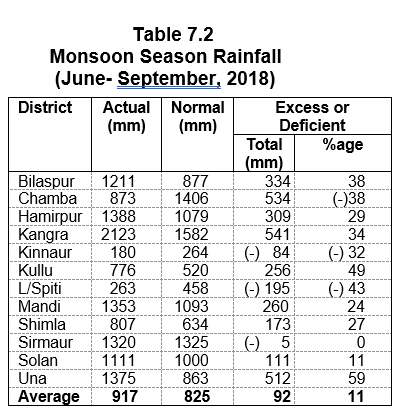
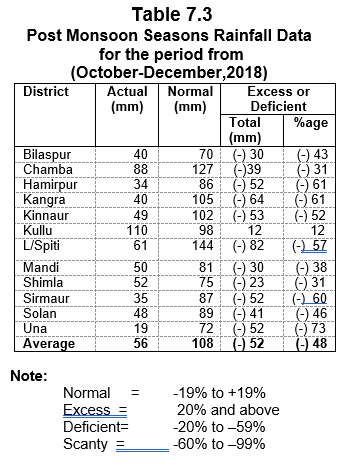
The State of Himachal is becoming a vibrant economy of the country due to the steady efforts of the simple and hardworking people of the State and progressive policies
of the Central and State Government. Today Himachal could become the most prosperous and fastest growing economy in the country. The economy of the State is expected to achieve
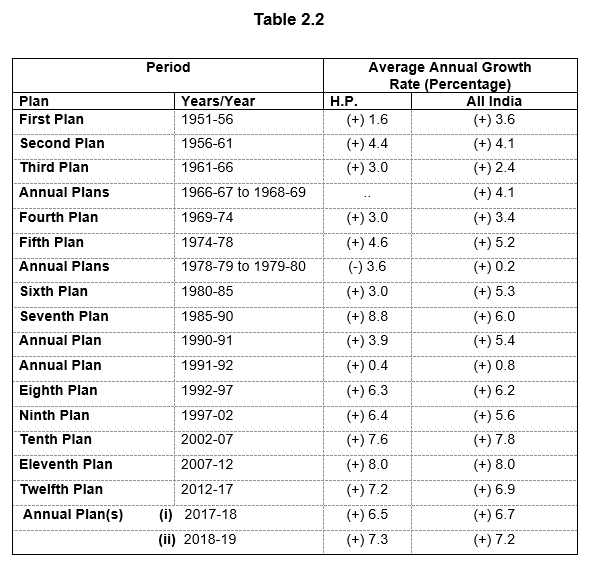
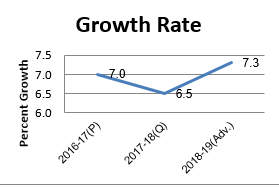
a growth rate of 7.3 percent in the current financial year 2018-19.
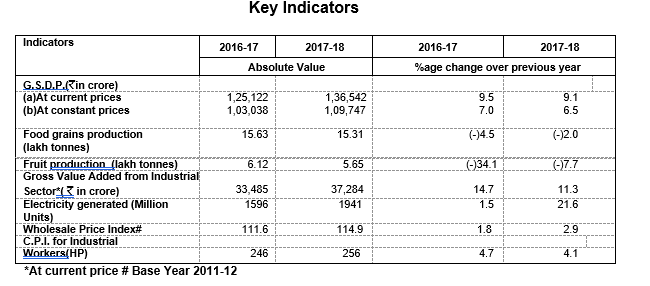
The State Gross Domestic Product (GSDP) at current prices, is estimated at `1, 36,542 crore in 2017-18 as against ` 1,25,122 crore in 2016-17 showing an increase of
9.1 percent during the year. At constant (2011-12) prices in 2017-18 is estimated at `1,09,747 crore as against `1,03,038 crore in 2016-17 registering a growth of
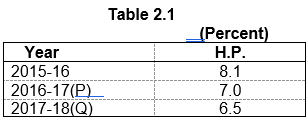
6.5 percent during the year as against the growth rate of 7.0 percent during the previous year. The increase in total State Domestic Product is mainly attributed to 20.4 percent
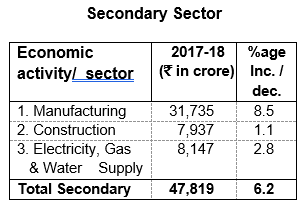
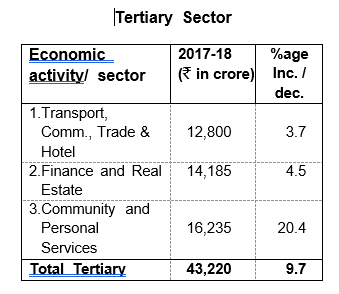
in Community & Personal Services sectors, 4.5 percent in Finance & Real Estate, 3.7 percent increase in Transport and Trade, 8.5 percent in Manufacturing sector, 1.1 percent in
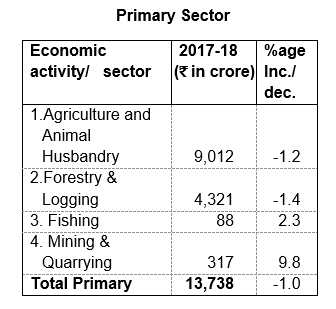
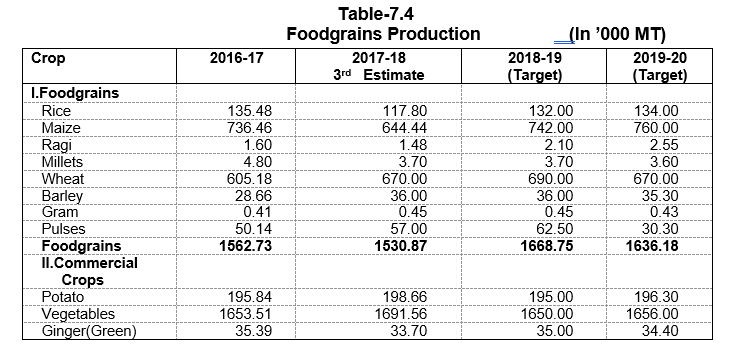
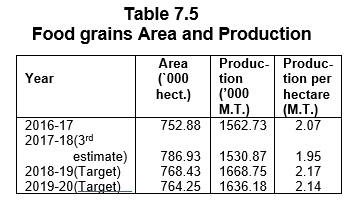
Construction and 2.8 percent increase in Electricity, Gas & Water Supply. Whereas the Primary Sector has shown a marginal decrease of 1.0 percent. Food-Grains production, which
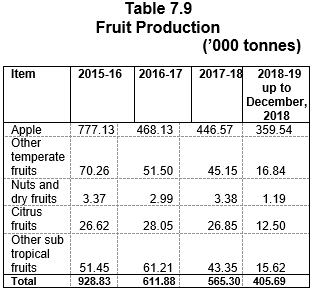
was 15.63 lakh MT during 201617 has decreased to 15.31 lakh MT during 2017-18 and is targeted at 16.69 lakh MT in 2018-19. The Fruit Production has decreased to 5.65 lakh MT
in 2017-18 as against 6.12 lakh MT in 2016-17, showing a decrease of 7.68 percent in 2017-18. The fruit production during 2018-19 (up to December, 2018) production was 4.06 lakh MT.
The per capita income at current prices witnessed an increase of 7.8 percent as it increased to ` 1,60,711 in 2017-18 from ` 1,49,028 in 2016-17.
As per the advanced estimates and on the basis of economic conditions up to December, 2018, the likely growth rate for 2018-19 will be around 7.3 percent.
The economic growth in the State is predominantly governed by agriculture and its allied activities showed not much fluctuations during nineties as the growth rate remained more
or less stable. The economy has shown a shift from agriculture sector to industries and services as the percentage contribution of agriculture and allied sectors in total State Domestic
Product has declined from 57.9 percent in 1950-51 to 55.5 percent in 1967-68, 26.5 percent in 1990-91 and to 8.8 percent in 2017-18.
The share of industries and services sectors respectively has increased from 1.1 & 5.9 percent in 1950-51 to 5.6 and 12.4 percent in 1967-68, 9.4 & 19.8 percent in 1990-91
and to 29.2 and 43.3 percent in 2017-18. However, the contribution of other remaining sectors declined from 35.1 percent in 1950-51 to 27.5 percent in 2017-18.
The declining share of agriculture sector do not, however, affect the importance of this sector in the State economy as the state economic growth still is being determined by the
trend in agriculture and horticulture production. It is the major contributor to the total domestic product and has overall impact on other sectors via input linkages, employment and trade etc.
Due to lack of irrigation facilities our agricultural production to a large extent still depends on timely rainfall and weather conditions. High priority has been accorded to this sector by the Government.
The State has made significant progress in the development of horticulture. The topographical variations and altitudinal differences coupled with fertile, deep and well drained soils favor the
cultivation of temperate to sub-tropical fruits. The region is also suitable for cultivation of
ancillary horticultural produce like flowers, mushroom, honey and hops.
During the year 2018-19 up to December, 2018, 4.06 lakh tonnes of fruits were produced in the State and it is envisaged to bring 2,004 hectares of additional area under fruit plants
against which 2,351 hectares of area has already been brought under plantation and 6.50 lakh fruit plants of different species were distributed up to December, 2018. Growing of off-season
vegetables has also picked up in the state. During the year 2017-18, 16.92 lakh tonnes of vegetables were produced as against 16.54 lakh tonnes in 2016-17 recorded a growth of 2.3 percent.
It is anticipated that the production of vegetables will be of the order of 16.50 lakh tonnes in 2018-19.
Himachal Pradesh continued to take ambitious steps to achieve its targets. In the area of climate change mitigation. The State action plans on climate change aim to create institutional
capacities and implement sectoral activities to address climate change.
In view of the growing need of the State economy, the Government has embarked upon a programme to provide
uninterrupted continuous access to power supply in the state. Several steps have been taken for increasing power generation, strengthening of transmission and distribution.
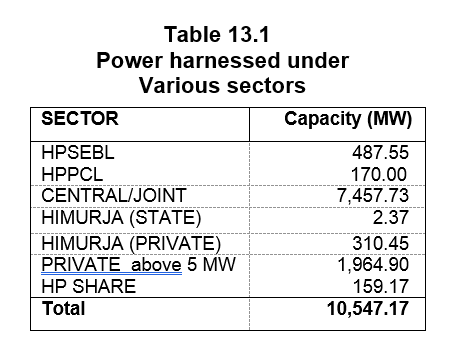
As a source of energy, hydro power is economically viable, nonpolluting and is environmentally sustainable. In order to restructure the sector, the Power Policy of the State attempts
to address all aspects like capacity addition energy security, access and availability, affordability, efficiency, environment and assured employment to people of Himachal.
Though the private sector participation in terms of investments in this sector has been encouraging but the smaller projects has been reserved for investors from Himachal Pradesh only
(up to 2 MW) and preference will be given for projects up to 5 MW.
Tourism is a major engine of economic growth, an important source of revenue earnings and a generator of employment of diverse kinds. The State Govt. has also developed
appropriate infrastructure for its development which includes provision of public utility services, roads, communication network, airports, transport facilities, water supply and
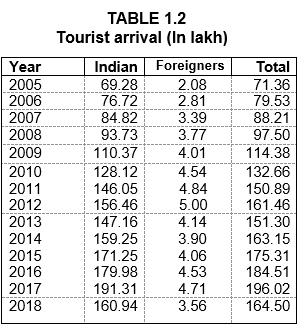
civic amenities etc. As a result of high profile media thrust, a significant rise has been noticed in the domestic as well as foreign tourist inflow during last few years is as below:- TABLE 1.
Information Technology has a great scope for employment generation and revenue earnings. The HIMSWAN provides various G2G, G2C, G2B, e-Procurement and eSamadhan etc.
systems to bring efficiency and transparency in administration. 2095 Government offices across the State has been connected through HIMSWAN net work.
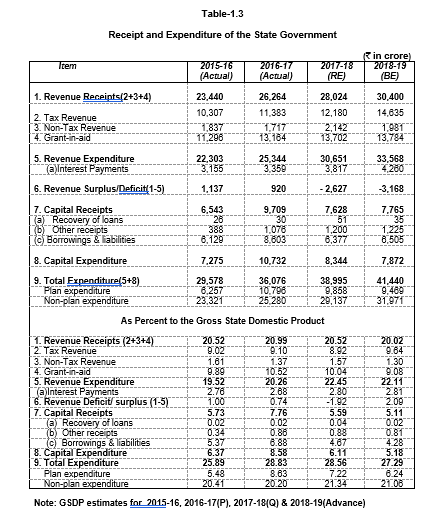
The annual plan for 2019-20 has been proposed at `7100.00 crore which will be 12.7 percent higher than the plan size of current year 2018-19.
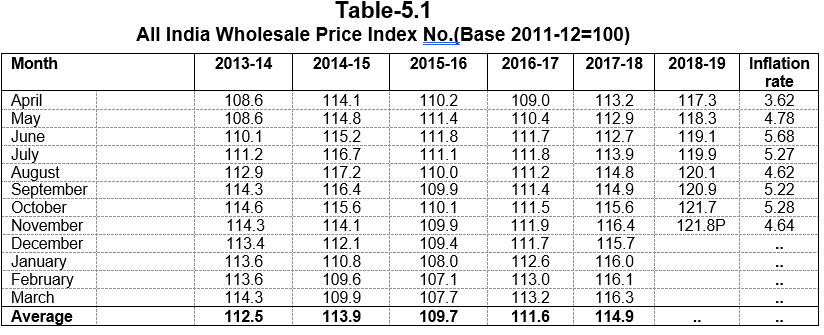
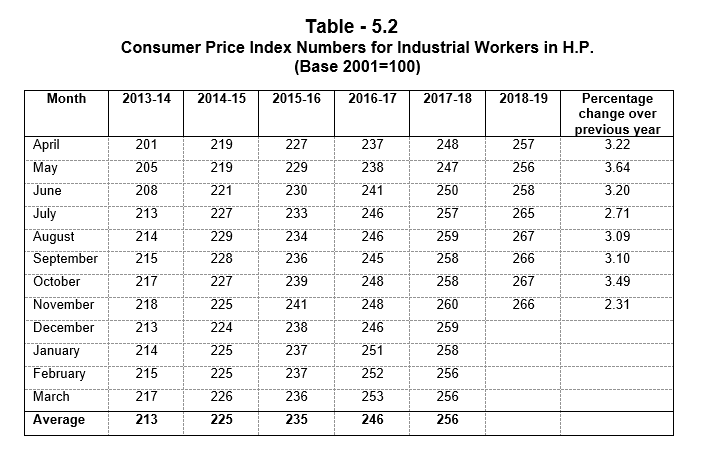
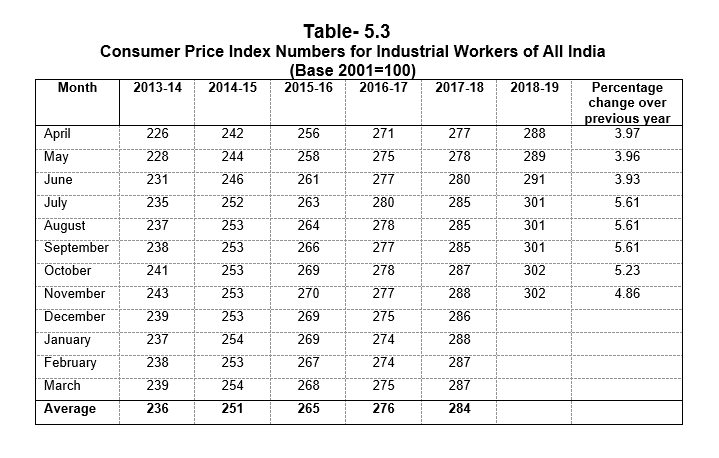
Containment of prices is on the priority list of Government. Inflation in Himachal Pradesh based on Working Class Consumer Price Index number during 2018-19 increased by 2.3
percent in November, 2018 as against 4.9 percent at National level.
The priority of the government has always been for social welfare programmes.
Concerted efforts have been made to improve the efficiency and
quality of public services delivery.
Some of the major achievements taken during the year are:-
1) The Government of Himachal Pradesh has implemented Good Governance Index.
2) ‘Shakti Button App’ and ‘Gudia helpline’ has been launched by Government of Himachal for the protection of women.
3) To deal strongly with the forest, mining and drug mafia,
‘Hoshiar Singh helpline’ 1090 has been started.
4) An online monitoring system
“Him Pragti” has been started for the monitoring of the welfare schemes, employment generation and Jan-Manch.
5) Mobile app facility launched for anganwari centres.
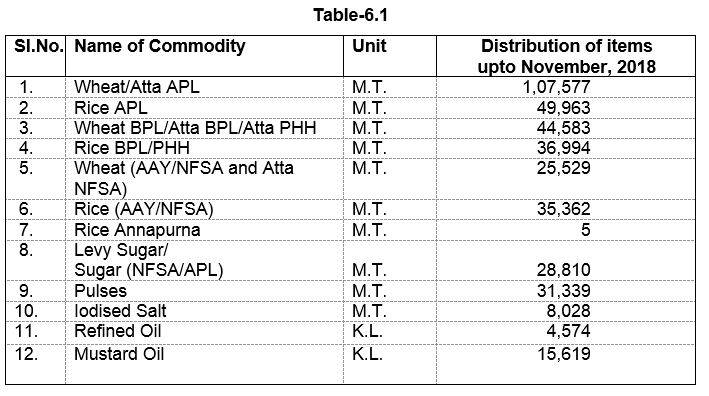
6) “E–P.D.S.” H.P. Mobile App has been launched in the State to provide easily subsidised ration, monitor and ensure its quality to more than 70 lakh consumer of the State.
7) To make the tourists familiar with the ancient cultural heritage of the State, and to train the local youngsters as cultural guide with the objective to provide them self
employment, a scheme named
‘Aaj Purani Rahon Se’ has been started.
8) The
‘Point of Sale’(POS) machines have been installed in all the fair price shops of the State.
9) New Women Police Stations have been opened in Solan, Chamba and Hamirpur districts.
10) A comprehensive campaign has been initiated against drug addiction and antidrug treatment has been started in the State.
11) Under the
‘Social Security Pension’ scheme the age limit for getting pension without any income limit reduced from 80 to 70 years.
l2) Social Security Pension has been increase to `750/- and under this scheme 76,025 new
pension cases have been sanctioned and total eligible beneficiaries are now 4,90,022 persons. The pension of age 70 years and above and 70 percent specially abled eligible persons has been enhanced to `1,300 per month.
13) The maternity leave of women employees on contact basis has been increased from 135 days to 180 days.
14) The minimum wages of the workers increased to ` 225/-.
15) Every month the problems of the people are settled on the spot through “Janmanch” under the Chairmanship of ministers.
16) Under
“Himachal Grihani Suvidha yogna” 32,134 new LPG connections have been provided in the State up to Nov, 2018.
17)Under
“Ujwala Yogna” of the Union government, 85,421 LPG connections have been provided.
18) A decision has been taken to provide two sets of smart uniform, free of cost to more than 9 lakhs students of class 1st to 10+2.
19) Nursery and KG classes have been started in selected 3,391 schools of the State, in which 23,800 children have been enrolled, under this pre-primary programme.
20) In the State out of 137 Degree Colleges the free Wi-Fi facility has been provided in 114 colleges.
21) Him Care scheme has been introduced in the State for those families which are not covered under
Aayushman Bharat Yojna or any other Health compensatory Scheme.
Under this scheme any family member admitted as an indoor patient in hospital, will get free treatment up to ` 5 lakh.
22) To provide different medical test facilities to the citizens
“Mukhya Mantri Nirog Yojna” has been started. Under this scheme 130 WELLNESS centres will be setup in the state.
23) 108 Bike Ambulance Service has been started in the State. Himachal is the first State to introduce this service in North India.
24) Tele-Medicines facilities has been started in the 25 Health Sub Centres of Shimla,Sirmaur and Chamba Districts and tribal area of Kilarh, through this facility 29,000 people have been benefitted.
25) Yoga facility has been started in selected 471 Ayurvedic Health Centres after witnessing its importance.
26) To promote organic farming in the State a new scheme
“Prakritik Kheti Khush-haal Kissan” has been started in the State by allocating `25 crore in the State budget.
27) 10.31 lakh Soil health cards have been distributed to the farmers.
28) M-kisan mobile portal scheme has been launched in the State to provide latest technical information to the horticulturists of the State.
6.90 lakh farmers have been registered under this scheme.
29) Heli-Taxi service has been started for the tourists from Shimla to Chandigarh and Chandigarh to Shimla.
30) To encourage the youngsters towards entrepreneurship
“Mukhya Mantri Swavlamban Yojana” has been started.
31) Under
“Mukhya Mantri Start-Up Yojana” 27 Start-ups have been started in 8 Incubation Centres and 3 promising entrepreneurs have been awarded.
32) One Battalion of National Disaster Reaction Force has been sanctioned.
33) Dev Bhumi Darshan Yojna for the senior citizens of the age over 70 years to visit the religious places has been started.
34) State has received three prizes for excellent work done with respect to
Pradhan Mantri Gramin Sarak Yojna.
35) State has received first prize for excellent work with respect to
Pradhan Mantri Gramin Aawas Yojna.
36) State has received four prizes for extraordinary performance in the field of health.
37) The Per Capita Income has touched the level of `1,60,711 in 2017-18 witnessing a growth of 7.8 percent over 2016-17 and is estimated at
`1,76,968 in 2018-19.