In a short span of time of Himachal Pradesh has become a model of development not for smaller States but for
the bigger States of the country in the field of Education, Health, Horticulture, Social Welfare and inclusive
growth. Today Himachal is known as most prosperous and fastest growing economy in the country. The economy of
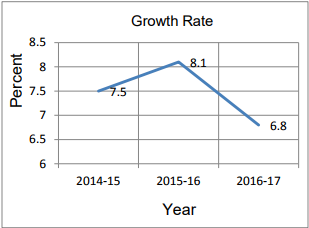
the State is expected to achieve a growth rate 6.8 percent in the current financial year .
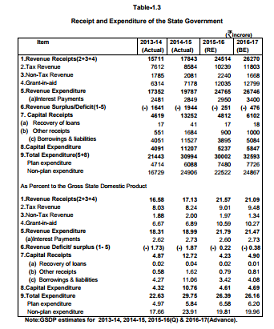
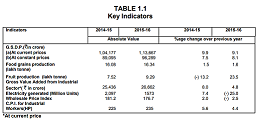
The State Gross Domestic Product (GSDP) at factor cost at current prices, the GSDP is estimated at
`1,13,667 crore in 2015-16 as against `1,04,177 crore in 2014-15 showing an increase of 9.1 percent during the
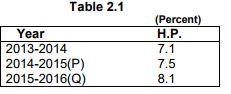
year. At constant (2011-12) prices in 2015-16 is estimated at `96,289 crore as against `89,095 crore in 2014-15
registering a growth of 8.1 percent during the year as against the growth rate of 7.5 percent during the previous year.
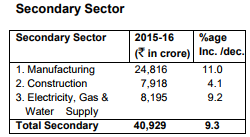
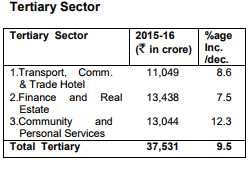
The increase in total State Domestic Product is mainly attributed to 12.3 percent in Community & Personal Services sectors,
11.0 percent in manufacturing sector, 9.2 percent increase in Electricity, Gas & Water Supply, 8.6 percent increase in Transport and Trade,
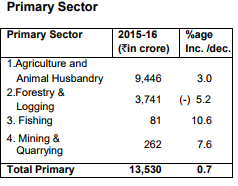
7.5 percent in Finance & Real estate. Whereas the Primary sector has shown a marginal increase of 0.7 percent.
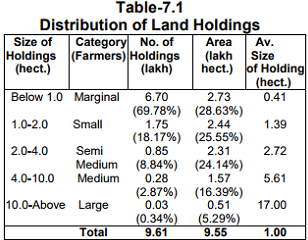
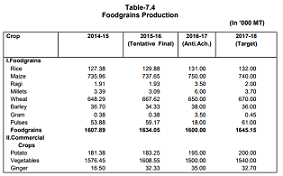
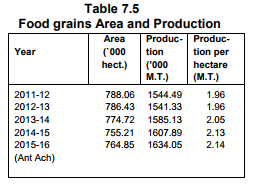
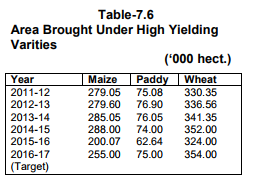
Food-grains production, which was 16.08 lakh MT during 2014-15 has increased to 16.34 lakh MT during 2015-16 and
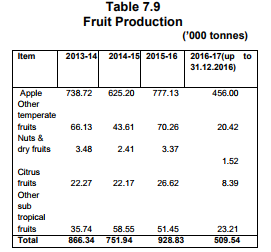
is targeted at 16.45 lakh MT in 2016-17. The fruit production has increased by 23.5 percent i.e from 7.52 lakh MT in
201415 to 9.29 lakh MT in 2015-16 and during 2016-17 (up to December, 2016) production was 5.10 lakh MT.
The Per Capita Income at current prices witnessed an increase of 9.1 percent as it increased to `1,35,621 in 2015-16 from `1,24,325 in 2014-15.
As per the advanced estimates and on the basis of economic conditions up to December, 2016, the likely growth rate for 2016-17 will be around 6.8 percent.
The economic growth in the State is predominantly governed by agriculture and its
allied activities showed not much fluctuations during nineties as the growth rate remained more or less stable. The economy has
shown a shift from agriculture sector to industries and services as the percentage contribution of agriculture and allied sectors
in total State Domestic Product has declined from 57.9 percent in 1950-51 to 55.5 percent in 1967-68, 26.5 percent in 1990-91 and to 9.4 percent in 2015-16.
The share of industries and services sectors respectively has increased from 1.1 & 5.9 percent in 1950-51 to 5.6 and 12.4
percent in 1967-68, 9.4 & 19.8 percent in 1990-91 and to 25.2 and 43.9 percent in 2015-16. However, the contribution of other remaining
sectors showed a favourable shift i.e. from 35.1 percent in 1950-51 to 21.5 percent in 2015-16.
The declining share of agriculture sector do not, however, affect the importance of this sector in the state economy as
the state economic growth still is being determined by the trend in agriculture and horticulture production. It is the major
contributor to the total domestic product and has overall impact on other sectors via input linkages, employment and trade etc.
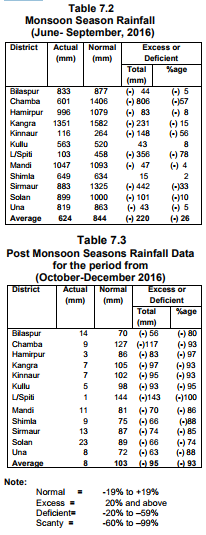
Due to lack of irrigation facilities our agricultural production to a large extent still depends on timely rainfall and weather conditions.
High priority has been accorded to this sector by the Govt.
The State has made significant progress in the development of Horticulture. The topographical variations and
altitudinal differences coupled with fertile, deep and well drained soils favour the cultivation of temperate to sub-tropical fruits.
The region is also suitable for cultivation of ancillary horticultural produce like flowers, mushroom, honey and hops.
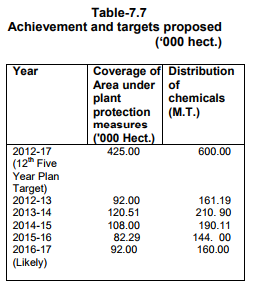
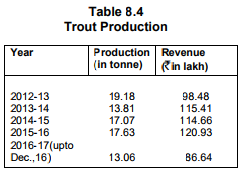
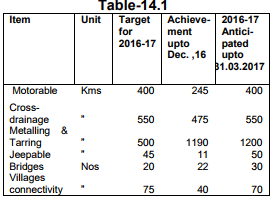
During the year 2016-17 up to December, 2016, 5.10 lakh tonne of fruits were produced in the state and it is envisaged to bring
3,000 hectares of additional area under fruit plants against which 2,817 hectares of area has
already been brought under plantation and 7.53 lakh fruit plants of different species were distributed up to December, 2016.
Growing of off-season vegetables has also picked up in the state. During the year 2015-16, 16.09 lakh tonne of vegetables
were produced as against 15.76 lakh tonne in 2014-15 recorded a growth rate of 2.1 percent. It is anticipated that the
production of off season vegetables will be of the order of 15.00 lakh tonne in 2016-17.
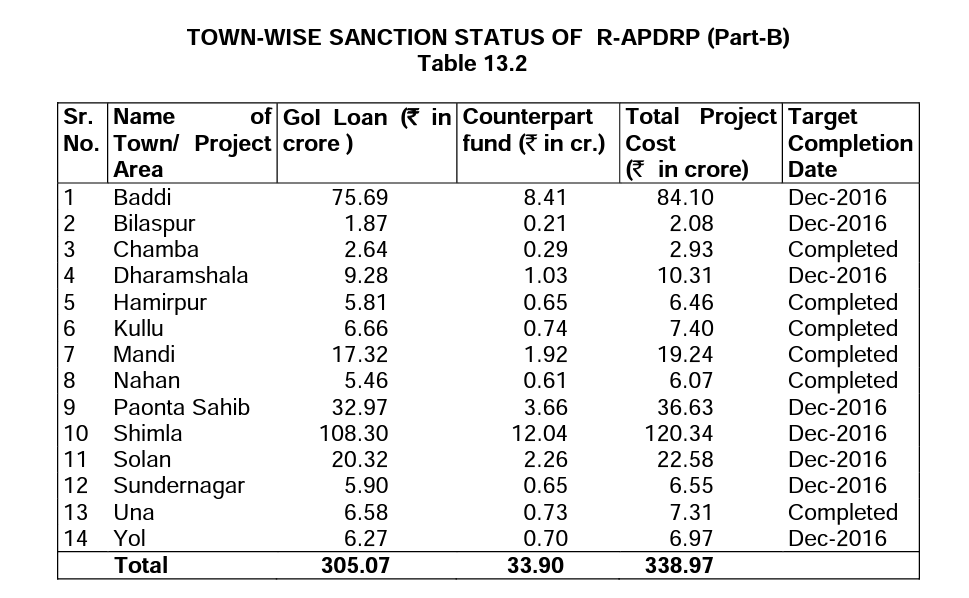
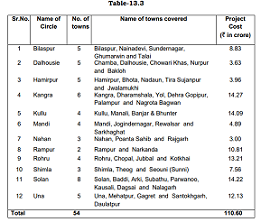
In view of the growing need of the State economy, the government has embarked upon a programme to provide uninterrupted
continuous access to power supply in the state. Several steps have been taken for increasing power generation, strengthening of
transmission and distribution. As a source of energy hydro power is economically viable, nonpolluting and is environmentally
sustainable. In order to restructure the sector, the Power Policy of the State attempts to address all aspects like capacity
addition energy security, access and availability, affordability, efficiency, environment and assured employment to people of
Himachal. Though the private sector participation in terms of investments in this sector has been encouraging but the smaller
projects has been reserved for investors from Himachal Pradesh only (up to 2 MW) and preference will be given for projects up to 5 MW.
1
Himachal Pradesh continued to take ambitious targets in its actions in the area of climate change mitigation. The State action plans
on climate change aim to create institutional capacities and implement sectoral activities to address climate change.
Information Technology has a great scope for employment generation and revenue earnings. The HIMSWAN provides various G2G,
G2C, G2B, e-Procurement & e-Samadhan etc. systems to bring efficiency and transparency in administration.
1
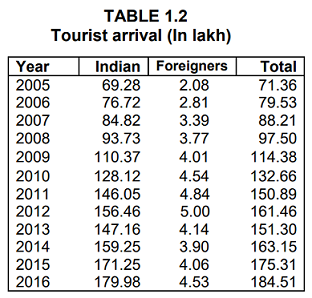
Tourism is a major engine of economic growth, an important source of revenue earnings and a generator of employment of diverse kinds.
The State Govt. has also developed appropriate infrastructure for its development which includes provision of public utility services, roads,
communication network, airports, transport facilities, water supply and civic amenities etc. As a result of high profile media thrust, a
significant rise has been noticed in the domestic as well as foreign tourist inflow during last few years as below:-
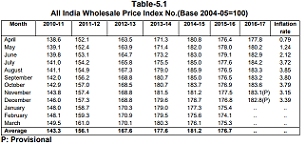
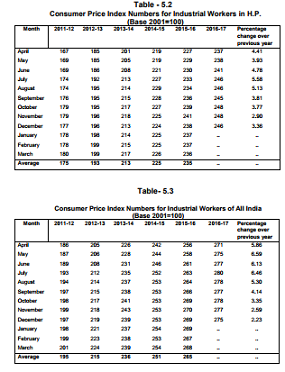
Containment of price is on the priority list of government. Himachal
Pradesh Working Class Consumer Price Index number during 2016-17 increased by 3.4 percent in December, 2016 as against 2.2 percent at National level.
The annual plan for 2017-18 has been proposed at `5,700.00 crore which will be
9.6 percent higher than the plan size of current year 2016-17.
To fulfil the commitments towards public, a separate department of Redressal and Public Grievances under the direct supervision
of the Hon’ble Chief Minister has been set up in each of the public service oriented Departments to make this more efficient. Himachal
Pradesh is the first state in the country to launch e-samadhan for redressal of public grievances.
The priority of the government has always been for Social Welfare programmes. Concerted efforts have been made to improve the
efficiency and quality of public services delivery.
Major achievements on the path of Socio-Economic resurgence are:-
1) The State has been adjudged best State in Education and inclusive growth in the country.
2) Himachal has been declared second State under Open Defecation.
3) Under Smart City Mission Municipal Corporation Dharmashala has been approved by Government of India.
4) Under “Public Service Guarantee Act” 119 services in 20 departments has been implemented for efficient and timely solutions.
5) Himachal is the first State in the country to do away with the affidavits, where courts conditions are not necessary.
6) Social Security Pension increased from `600 to ` 650 per month.
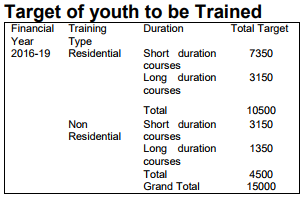
7) Under the skill development scheme an allowance of `116 crore has been distributed to 1,58,100 beneficiaries.
8) All persons above the age of 80 years and above are being provided an old age pension of `1,200 per month irrespective of
any income limit except those drawing any other pension.
9) 7.14 lakh Kisan Credit Cards have been issued by the banks.
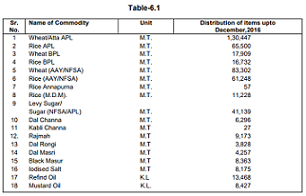
10) Essential commodities are being supplied on subsidized rates to 18,26,390 ration card holders in the State so as
to save them from the on- slaught of rising prices.
11) Under Rajeev Gandhi Ann Yojna identified beneficiaries are being provided rice at the rate of `3/- per Kg and wheat
` 2/- per Kg every month.
12) To save and promote agriculture activities from the menace of stray animals, wild animals and monkeys the government
has introduced the “Mukhya Mantri Khet Sarkasan Yojna” under 60:40 ratio.
13) Under Restructured weather Based Crop Insurance Scheme(R-WBCIS) total of 2,33,378 number of farmers have been covered till
Rabi crop in 2016-17 season.
14) To bring diversification in horticulture industry an area of 79.693 hectares has been brought under flower cultivation upto December, 2016.
15) To protect the horticulture produce from hail storms the government is providing subsidy of 80 percent on anti-hail nets.
16) The WBCIS is being implemented in 36 blocks for apple, 41 blocks for Mango, 15 blocks for Kinnow, 13 blocks for Plum and 5 blocks for Peach crops.
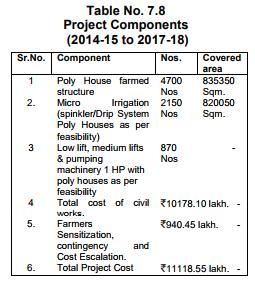
17) To increase the productivity and quality in Horticulture, the World Bank has funded `1,169.15 crore project.
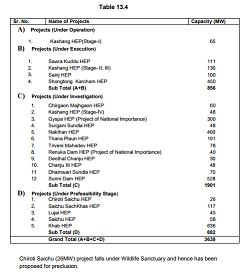
18) During the financial year 2015-16, 1,573 million units of electricity were generated.
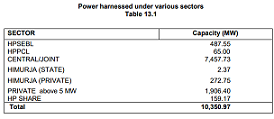
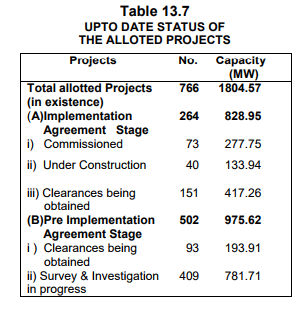
19) 10,351 MW hydro power has been harnessed out of 27,436 MW identified potential which comes out to 37.73 percent.
20) 10 L.E.D bulbs are being provided to domestic consumers at cheaper rate from market.
21) Investor meets organized in Mumbai, Bangluru, Ahmedabad and New Delhi.
22) Under Mahatama Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee scheme 160.31 lakh Mandays have been generated by providing Employment to 4,31,933 households.
23) Under Rajiv Awaas Yojana 846 houses are being constructed in the State during current financial year.
24) A new scheme of Mukhya Mantri Awaas Yojana has been started in the current financial year for the general category BPL families. The unit cost of this scheme is `1,30,000/-
25) Swachh Bharat Mission is being implemented in all the 12 districts of the State in project mode and Himachal is considered as a leading State in the field of Sanitation.
26) Under Matri Shakti Bima Yojna all women in the age group of 10-75 years, living below poverty line are covered in case of their death or special ability.
27) Under Lal Bahadur Shastri Kamgar Avam Shahari Ajivika Yojna, an amount of `1.50
crore has been provided for wage employment in newly created/ merged areas of Municipal Councils/ Corporations in the Pradesh.
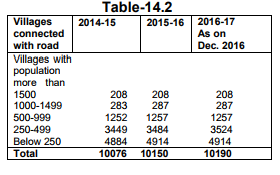
28) 1,416 Kms roads/ paths/ streets and drain are being maintained by 54 Urban Local Bodies.
29) 208 beneficiaries were provided skill training under National Urban Livelihood Mission.
30) Special attention is being given to quality education and to achieve the target of universalization of
elementary education under Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan is vigoursly implemented
31) A programm named Prayas for the popularisation and innovation in Science and Math was launched for students of 6 to 8 class.
32) Free education is being provided to girl students in the State upto University level.
33) The girl students studying in classes IX to XII belonging to SC, ST, OBC, minority communities
and BPL families are being provided with hostel facilities in the educationally backward blocks.
34) Under Post Matric Scholarship to SC/ST/OBC a total of 52,969 students have been benefitted.
35) Under Rajiv Gandhi Digital Vidyarthi Yojna the student of 10th & 12th have been provided 10,000 Notebooks.
36) To improve the quality education two govt., Sr. Sec. Schools have been designated as Aadrash Model Schools
in each Constituency of each district.
37) To improve the educational status of the deprived section of the society, various types of scholarships/
stipend are being provided by the State/ Central government at various stages.
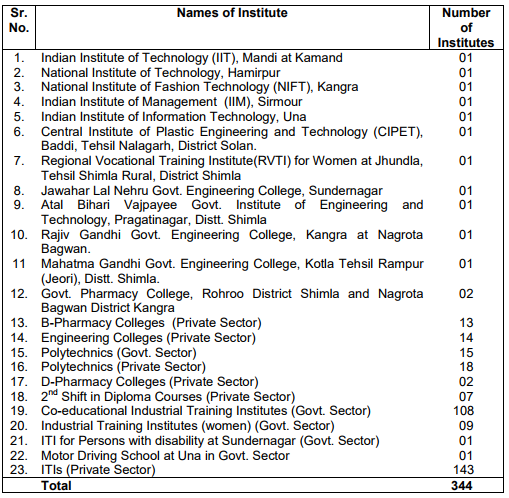
38) Three Medical colleges are being opened in districts of Chamba, Sirmaur and Hamirpur.
39) The State government has taken over the ESI Medical College in Mandi district.
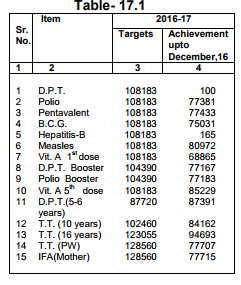
40) Under National Rural Health Mission 95 Health Institutions are identified to provide 24 hours emergency services.
41) More than one lakh smart cards have been issued under Mukhya Mantri State Health Care Scheme to the selected families .
42) Under “BETI HAI ANMOL Yojna” 11,359 girls have been benefitted.
43) BETI BACHAO BETI PADHAO has been started in Una district of the Pradesh. Now this scheme has also been started in Kangra and Hamirpur districts.
44) Under Mukhya Mantri Kanyadaan Yojna 1,314 beneficiaries were covered upto December, 2016.
45) Inter caste marriage grant has been increased from `25,000 to `50,000. During the current year 277 couples have been benefitted.
46) Under Indira Gandhi Matritva Sahyog Yojna there is provision of cash incentive of `6,000 and so far 4,717 women have been benefitted.
47) To provide financial assistance and support services to Rape victims an amount of `75,000 is being provided and 56 women have been benefitted under this scheme.
48) 23,875 childern have been benefitted under Mother Teressa Asahay Matri Sambal Yojana in the current financial year.
49) In order to ensure accountability, transparency, efficiency and to improve service delivery mechanism to general public
Web services has been started for all planning & special areas in the State.
50) 25 percent exemption in bus fare for woman in road transport has been started.
51) Under Rajiv Gandhi Panchyat Sashaktikaran Abhiyan the newly elected representatives of Panchyati Raj Institutions will be provided training.
52) Himachal is the only State which has provided horizontal connectivity to 1,860 government offices in the State.
53) Under State Portal and State Services Delivery Gateway, 57 G2C services have been made available through this portal at www.eserviceshp.gov.in
54) Under Aadhaar scheme UID has been generated for more than 72.46 lakh (100.69 percent) residents against the projected population of 2015.
55) Public Services Delivery Helpline has been set up for the people of the State.
56) A facility of Toll Free telephone number has been set up for reporting the cases of corruption in the government departments.
57) The Per Capita Income has touched the level of `1,35,621 in 2015-16 witnessing a growth of 9.1 percent over 2014-15 and is estimated at `1,47,277 in 2016-17.